

The most important examination for a woman's health
Regular gynecological examinations are important for maintaining the health of every woman. They serve to detect unwanted changes in the reproductive organs and allow for timely treatment.
Regular gynecological examinations are important for maintaining the health of every woman. They serve to detect unwanted changes in the reproductive organs and allow for timely treatment.
A gynecological examination can detect abnormal changes in the external and internal genital organs, such as changes in the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia, bleeding, the presence of tumors, and the like.
Preventive regular gynecological examination is also extremely important for the early detection of premalignant cervical lesions.
Cervical cancer in Croatia is diagnosed every day in one woman, and one woman dies from it every third day.
It is recommended to perform a gynecological examination at least once a year in accordance with the gynecologist’s recommendation, the results of the Pap smear and gynecological ultrasound.
Gynecological examination includes:
Like any medical examination, a gynecological examination begins with a conversation with a specialist doctor.
In our Gynecology Clinic , we place special emphasis on this part of the examination. This is an opportunity to achieve quality communication with your doctor who is fully dedicated to answering all your questions and concerns.
We recommend that you entrust all ailments to the doctor in detail without fear and discomfort. Our specialists emphasize an individual approach and will be ready to offer you their expert advice.
After talking to the doctor, women who have had sexual intercourse are examined on a gynecological table consisting of 2 parts. First, a visual examination of the external genitalia is performed, i.e. the labia minora and majora, the clitoris and the external opening of the vagina.
This is followed by an examination using a speculum. It is an instrument in the shape of a duck’s beak, made of metal or plastic. It allows the walls of the vagina to be spaced apart to examine the inside of the vagina and visualize the cervix. Examination in speculum takes only a few minutes and is usually not painful.
During the speculum examination, a Pap smear is also performed. A swab of the vagina, cervix and cervical canal is taken and sent for cytological analysis.
A Pap smear can detect the presence of inflammatory conditions and some sexually transmitted diseases. Primarily, however, it serves to detect abnormal cells that may indicate premalignant lesions or cervical cancer.
The examination in the speculum is followed by the second part of the vaginal examination, the so-called bimanual examination. The gynecologist carefully enters the vagina with the index and middle fingers of one hand, and presses the lower abdomen from the outside with the other hand. In this way, the size, shape and position of the uterus, ovaries and vagina are determined.
This part of the examination should also not be painful. In the event that pain occurs, it is necessary to communicate it to the gynecologist and point out the exact area in which the pain occurs and in what circumstances.
An indispensable part of the gynecological examination is gynecological ultrasound. It is most often done with a vaginal ultrasound probe that is inserted into the vagina, and the internal genital organs inaccessible to eye examination (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes) are shown. During a vaginal ultrasound examination, it is recommended to have an empty bladder.
Gynecological ultrasound provides insight into the size, shape and thickness of the uterine wall, as well as the appearance, location and size of the ovaries.
Before the examination, at home it is advisable to wash the intimate area with warm water and mild soap. In doing so, it is important not to rinse the inside of the vagina and it is necessary to avoid aggressive agents as this can affect the result of the Pap smear.
Generally speaking, the intimate area does not need to be waxed because it is not important in a gynecological examination. We advise you to do what is most comfortable for you.
Given that you will have to take off your clothes in the changing room before the examination, it is advisable to wear comfortable and practical clothing such as a skirt, dress or longer tunic.
At least 24 hours before the gynecological examination, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse. The examination is best done in the first part of the menstrual cycle (immediately after menstruation) so that the results of the Pap smear and gynecological ultrasound are more accurate and reliable.
We recommend that you make a list of questions at home that you want to ask the gynecologist. It is not uncommon for important questions to be forgotten during the examination due to excitement or fear.
Gynecological examination is often associated with fear and discomfort, especially pronounced in young women who visit a gynecologist for the first time.
Part of the discomfort is caused by the fear of the unknown and the fact that it is an examination of the intimate area. However, the first examination by a gynecologist can be quite a pleasant experience.
The first visit to the gynecologist for women who have not had sex and do not have acute problems does not necessarily end with a gynecological examination. In the conversation, given the reason for coming, the gynecologist will assess whether a gynecological examination is necessary or not.
For women who have not had sex, it is primarily a conversation with a specialist doctor, during which they can find out reliable information about contraception, sexual health preservation and what to expect in case of planning sexual intercourse.
Keep in mind that the gynecologist is there for you as a medical professional and will not judge you regardless of the problems, doubts or fears you encounter. Use the conversation to ask all the questions you are interested in.
Plan your first gynecological exam in between On the 7th and 12th day of the menstrual cycle . Write down the date of your last menstrual period, as this will certainly be one of the main questions your gynecologist will ask you.
As a rule, women who have not had their first sexual intercourse are not examined through the vagina, but only the external genitalia and the hymenal opening (hymen) are examined.
If the hymen is intact, it is not possible to do a bimanual examination of the internal organs through the vagina, so it is most often done through the colon, if necessary. In this case, gynecological ultrasound is also not performed transvaginally, but with an abdominal probe with a full bladder through the abdominal wall.
If gynecological ultrasound is done on the abdomen, it is necessary to come to the examination with a full bladder, or about half an hour before the examination, drink a larger amount of fluid.
In some cases, due to the thickness of the abdominal wall, it is not possible to perform a quality ultrasound examination, so it must be done through the large intestine. Today’s ultrasound probes are extremely thin, so the examination is performed with minimal discomfort for the patient.
Gynecological examination is an integral part of preserving reproductive and sexual health. It should be done regularly even when you have no problems, for the purpose of preventing diseases of the sexual and reproductive organs.
Although it is often associated with discomfort because it is a sensitive area, it is most often painless and plays a significant role in proper sexual health education.
The Gynecology Clinic of the Lohuis Filipović Polyclinic provides medical care using the most modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of women’s intimate health.
We especially nurture collaborative, teamwork that unites experience, knowledge and cutting-edge technology to respond to the specific needs of each patient.
Our goal is successful diagnosis, treatment, patient monitoring, and positive and long-term results.
Our multidisciplinary team brings together renowned experts with many years of experience in scientific and practical work.
There is no special age when a girl should go for the first gynecological examination, especially when she is not sexually active and there are no special problems. However, a gynecological examination also has a preventive and educational role
A gynecological examination is definitely recommended if the girl is planning or has become sexually active. An examination by a gynecologist is also recommended for advice when planning a pregnancy or when you want to be informed about all available methods of contraception.
In addition to the above, it is necessary to perform a gynecological examination when the following symptoms appear:
For girls in puberty, the indication for an earlier first gynecological examination may be the absence of signs of puberty, for example, the absence of breast development and other secondary characteristics (pubic and axillary hair) by the age of 15, the absence of the first menstrual period by the age of 13. Age.
The general recommendation is to perform a regular, preventive gynecological examination at least once a year.
In women over 35 years of age, a gynecological examination is recommended to be performed every year, while a Pap smear (if normal) can be performed once every 3 years.
In the period before, during and after menopause , it is advisable to perform a gynecological examination at least once every 2 years. Regular check-ups are extremely important during this period due to hormonal changes that occur as a result of the cessation of menstruation.
Pregnant women are recommended to have their first gynecological examination done between the 7th and 11th week of pregnancy to determine the location of pregnancy, duration and number of fetuses. If more than a year has passed since the last Pap smear, the gynecologist will repeat the swab.
If necessary, the gynecologist will also take a cervical swab for chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, aerobes and anaerobes, and refer you to perform basic laboratory tests such as complete blood count, urine tests, etc.
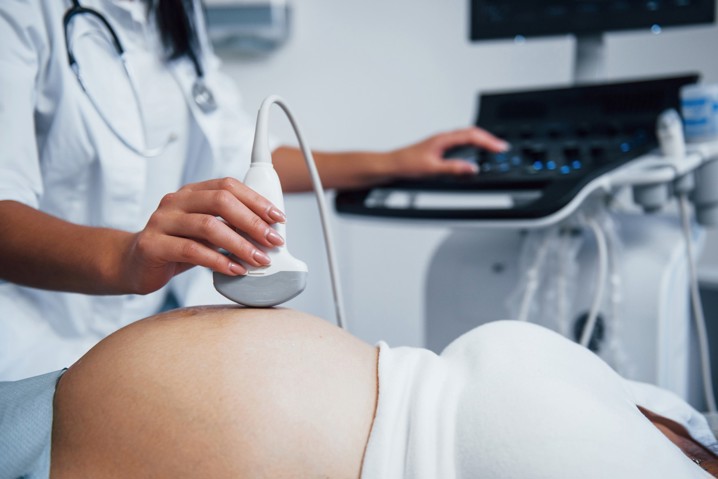

Gynecological ultrasound in pregnancy is extremely important because it enables early detection of deviations in fetal growth, anomalies and monitoring of the development of pregnancy.
Until the 38th week of pregnancy, a gynecological examination is performed every four weeks, as the birth approaches, the examinations are more frequent. From the 38th week of pregnancy, a gynecological examination is performed in the maternity clinic of the hospital where you want to give birth.
Menopause is a natural period of every woman’s life characterized by the absence of regular monthly bleeding. During this period, the reproductive ability ceases, the ovaries no longer produce eggs and the secretion of the female sex hormone estrogen is significantly reduced.
Perimenopause is the period preceding menopause when menstrual cycles become irregular, the physiological function of the ovaries gradually decreases. It usually occurs after the age of 40.
A gynecological examination during menopause is just as important for a woman’s health as it is during the reproductive period. There is a common occurrence of problems that are not talked about much in our environment, vaginal dryness, itching of the external genitals, problems with urine leakage.
Gynecological examination in menopause looks the same as in women of reproductive age, but more attention is paid to the examination of the external genitalia and vagina.
If you are in menopause and do not have acute health and gynecological problems, it is recommended to perform a gynecological examination every 2 to 3 years.
The main goal of LF Polyclinic is to improve the quality of life and health of our clients by providing them with top-notch healthcare services.