Removal of hyperpigmentation spots is possible with proper treatment
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation and is a common acquired skin disorder that manifests as bilateral, mottled, brownish pigmentation on the skin of the face.
This form of facial pigmentation was formerly called chloasma, but since it comes from the Greek language – meaning “to turn green”, the term melasma (brown skin) is preferred.
Melasma is more common in women than in men, and usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40.
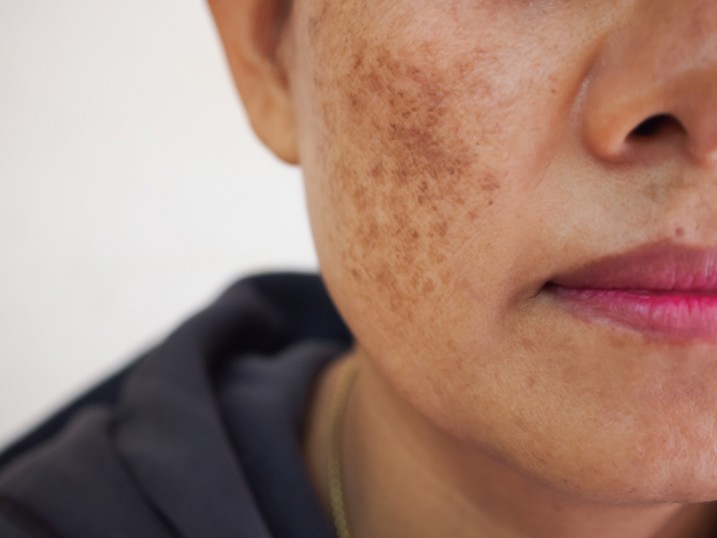
The cause of hyperpigmentation is complex – it is assumed that it is a disorder triggered by the process of photoaging in genetically predisposed individuals.
Pigmentation is ultimately the result of excessive melanin production by melanocytes (pigment cells), which are then stored by keratinocytes (epidermal melanosis) and/or deposited in the dermis area (dermal melanosis, melanophages).
Factors involved in the development of hyperpigmentation include:
Hyperpigmentation manifests itself as most often bilateral, asymptomatic, light to dark brown spots with regular or irregular edges.
In addition to the above, hyperpigmentation can have other clinical forms such as centrofacial hyperpigmentation (forehead, cheeks, nose, upper lip – the most common presentation), malar (cheeks and nose), mandibular (jawline and chin) and can also occur extrafacial in the area of the forearms, upper arms and shoulders.
Melasma can be divided into epidermal, dermal and mixed types, depending on the level of the skin where there is an increased concentration of melanin.
Epidermal melasma is characterized by:
Dermal melasma is characterized by:
Mixed melasma is the most common type of melasma, and is characterized by:
Due to its visibility, hyperpigmentation can seriously affect the quality of life of patients.
The diagnosis of melasma is usually made on the basis of the clinical appearance and additionally by examination with a Wood lamp and, if necessary, with a dermatoscope.
In case of uncertainty in the diagnosis, taking a small sample of the skin – a skin biopsy – is considered. A skin sample is taken and referred to a pathologist for histopathological verification.
Several treatment modalities are used to remove hyperpigmentation, the most important of which are general measures that include:
Local therapy
In the topical treatment of melasma, the best results are given by the use of a combined preparation containing hydroquinone, tretinoin and a local steroid of moderate strength (Kligman’s cream). In addition to the above, the use of azelaic acid in the form of a cream is also indicated.
”In-office” treatments
When removing hyperpigmentation, chemical peels can be applied. We distinguish between superficial, medium and deep peels. Superficial peels are mainly done with cocktails of various acids (fruit acids, resorcinol, azelic acid, etc.). Medium and deep peels are performed with trichloroacetic acid in different percentages, with or without the addition of phenols.
Of great importance is the use of the Q switch Nd-YAG laser, which targets only the pigment and with which there is no recovery time – you can immediately return to your daily activities.
Fractional lasers can also be used.
Treatment of melasma is demanding for both the patient and the doctor, given that the process is slow and time-consuming, especially if hyperpigmentation that has been present for a long time and hyperpigmentation that is located in the deeper layers of the skin are treated.
With these treatment modalities, it is possible to achieve a good therapeutic effect, but it should be borne in mind that the risk of melasma recurrence is high, especially if adequate year-round photoprotection is not performed.
For a consultation and examination with our expert team, you can contact us by phone at +3851 2444646 or via our online form.
Opening hours for appointments are Monday to Friday 10:15 a.m. – 6:15 p.m.
Contact us with confidence and let us come up with the best solutions and answers to all your questions together.